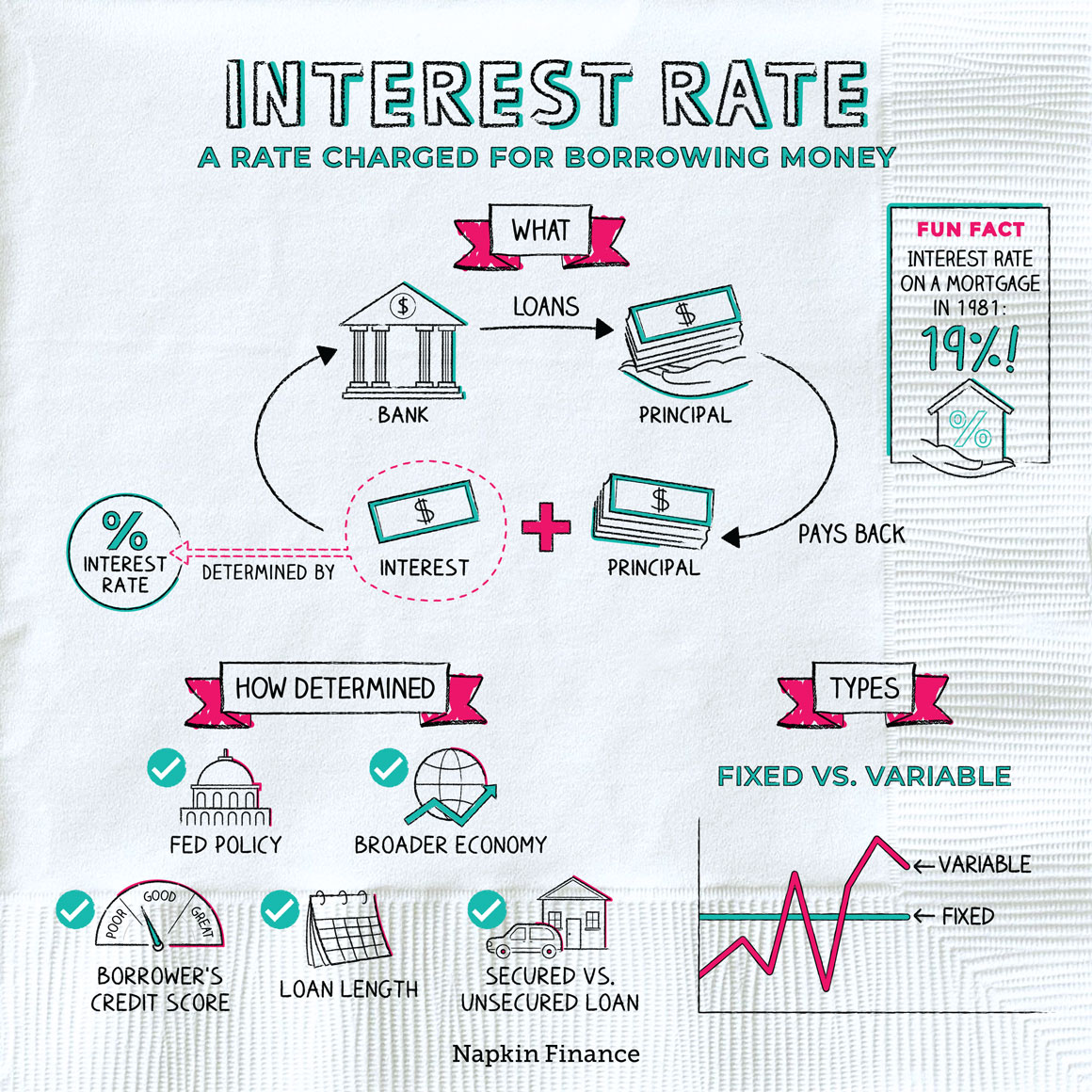
Interest rates
When an individual, organisation or country borrows money, goods, or property, the lender will usually want to make financial gain from giving them the money for that period, especially because they’re offering it as support to others, rather than investing it to generate income(=earn money). That is, they charge(=to ask an amount of money) the borrower for the use of an asset(=a useful or valuable thing). And so, they will apply an interest rate to the loan which they are supplying. An interest rate is the proportion of a loan that is charged in addition to the money they borrow, expressed as a percentage of the outstanding loan. Typically, interest rates are calculated on an annual basis(=every year) and are therefore referred to as the annual percentage rate (APR). Interest rates apply to most lending transactions; from mortgage(= borrowing money to purchase homes), launching a business, or even paying for university tuition fees - most of us will take out a loan at some point in our lives and pay interest as a result.